

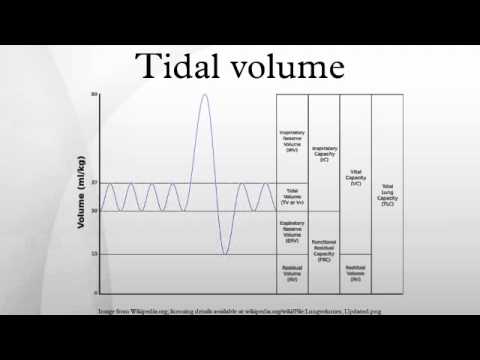
Tidal volume: that volume of air moved into or out of the lungs during quiet breathing (VT indicates a subdivision of the lung when tidal volume is precisely measured, as in gas exchange calculation, the symbol TV or V T is used.)įunctional residual capacity: the volume in the lungs at the end-expiratory position Vital capacity: the volume of air breathed out after the deepest inhalation. Inspiratory vital capacity: the maximum volume of air inhaled from the point of maximum expiration Inspiratory capacity: the sum of IRV and TV Inspiratory reserve volume: the maximal volume that can be inhaled from the end-inspiratory level Residual volume: the volume of air remaining in the lungs after a maximal exhalationĮxpiratory reserve volume: the maximal volume of air that can be exhaled from the end-expiratory position Tidal volume: that volume of air moved into or out of the lungs during quiet breathing (TV indicates a subdivision of the lung when tidal volume is precisely measured, as in gas exchange calculation, the symbol TV or V T is used.) Total lung capacity: the volume in the lungs at maximal inflation, the sum of VC and RV.

Every time a breath is taken, only a portion of the 500 mL of air ends up in the alveoli for gas exchange.
The Dead Space is the air volume in the respiratory tract that does not undergo gas exchange. In males, the air remaining inside the lungs is around 1200 mL, and in females, it is 1000 mL.

There is always some air inside the lungs to prevent the alveoli and bronchioles from collapsing. Residual Volume (RV): quantity of air that remains in the lungs after a forced exhalation. In males, this volume is around 1000 mL, and in females, it is 800 mL. IRV in males is about 3000 mL, while it is approximately 2000 mL in females.Įxpiratory Reserve Volume (ERV): the maximum amount of air that can be exhaled in addition to the TV during a hard expiration. Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV): the maximum amount of air that can be inhaled during a deep breath, in addition to the TV. This does not only explain why the breathing rate increases during physical activity but also why each breath is deeper. Increasing the Tidal Volume during exercise is the only way to exhale all the CO 2 over-produced. This volume of air can change, especially during exercise, due to the increase in carbon dioxide production by the body. A person at rest takes between 10 to 12 breaths per minute, and the amount of air inhaled and exhaled in each breath is approximately 500 mL for both males and females. Tidal Volume (TV): the amount of air taken in and out of the lungs during a normal and relaxed breath, also known as quiet breathing. These values are different in males, females, and kids and the ones used here as reference are those corresponding to an average male. Lung volumes refer to the amount of air that is normally exchanged by our lungs, which can be calculated as information about the health of a person.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
